The pancreas is a vital organ with dual roles in the body: it produces digestive enzymes essential for breaking down food, and it secretes hormones like insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. Maintaining pancreatic health is crucial for overall well-being, as it impacts digestion, nutrient absorption, and metabolic stability. Diet plays a pivotal role in supporting pancreatic function, with certain foods offering significant benefits through their nutritional content and bioactive compounds. Mohit Tandon from Burr Ridge suggested followings 10+ Good Food for your Pancreas:
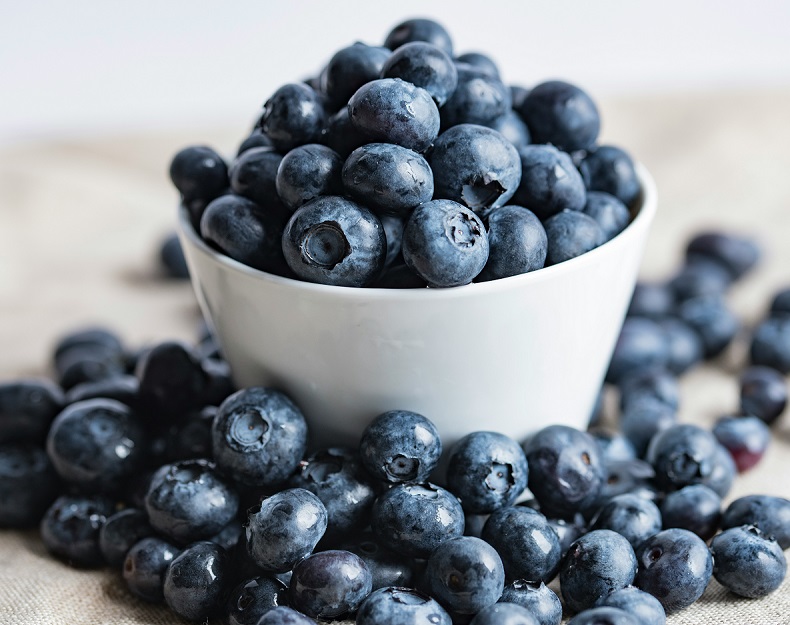
1. Blueberries
Blueberries are small, flavorful berries known for their high antioxidant content, particularly anthocyanins. These compounds help neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress in pancreatic tissues. By protecting pancreatic cells from damage, blueberries contribute to overall pancreatic health and may lower the risk of pancreatic disorders such as pancreatitis.
In addition to antioxidants, blueberries are rich in vitamins C and K, manganese, and dietary fiber. Vitamin C supports immune function and collagen synthesis, crucial for maintaining the integrity of pancreatic tissues. Meanwhile, dietary fiber aids digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the demand on the pancreas to produce insulin.
To incorporate blueberries into your diet, enjoy them fresh as a snack, add them to smoothies, yogurt, or oatmeal, or include them in salads for a burst of flavor and health benefits. – Mohit Tandon Burr Ridge

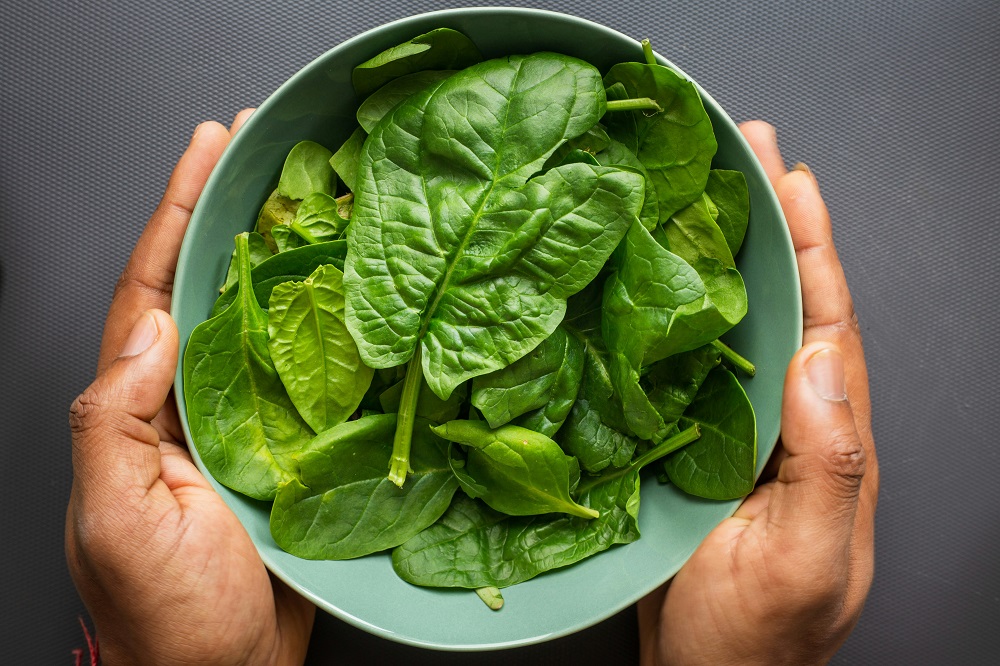
2. Spinach
Spinach is a nutrient-dense leafy green vegetable packed with vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals that support pancreatic health. It is particularly rich in vitamins A, C, and K, as well as folate, iron, and calcium.
Vitamin A in spinach plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy pancreatic tissues and supporting immune function. Vitamin C acts as a powerful antioxidant that protects pancreatic cells from oxidative stress. And Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting and bone health, contributing to overall metabolic stability.
Spinach also provides folate, which is necessary for DNA synthesis and cellular repair, and iron, which supports oxygen transport and energy production in cells. Calcium in spinach contributes to bone health and muscle function.
Incorporate spinach into your diet by adding it to salads, soups, stir-fries, or smoothies. Lightly cooking spinach helps retain its nutrient content while making it easier to digest and absorb its beneficial compounds.

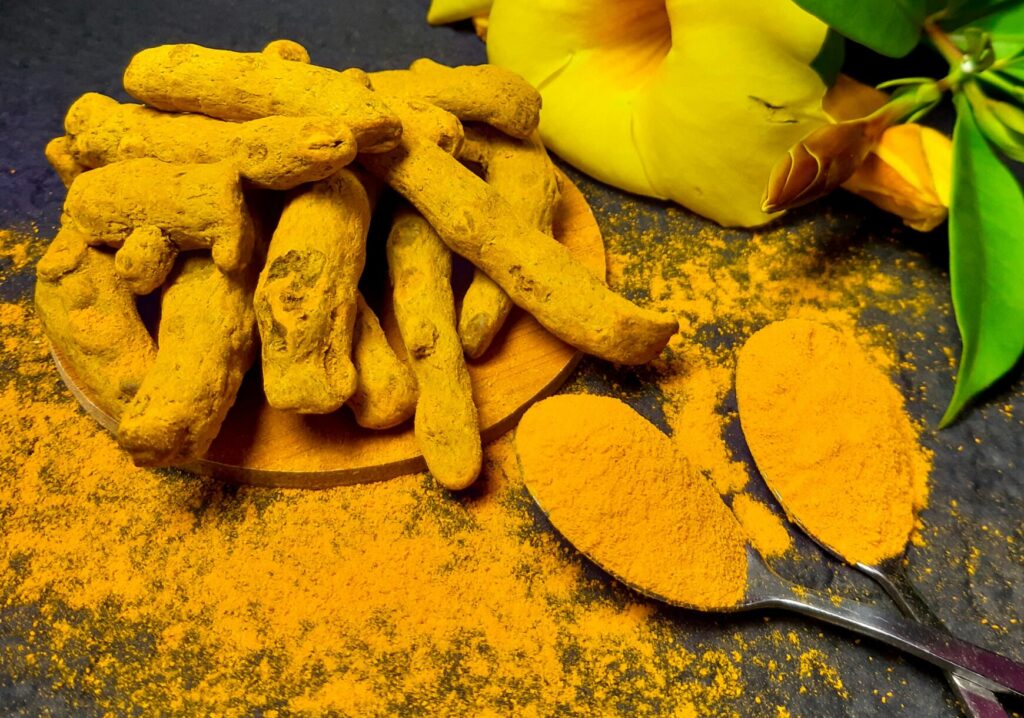
3. Turmeric
Turmeric is a bright yellow spice commonly used in Indian cuisine and traditional medicine. It contains curcumin, a potent bioactive compound known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Curcumin in turmeric helps reduce inflammation in pancreatic tissues by inhibiting inflammatory pathways. Chronic inflammation in the pancreas is linked to pancreatic disorders such as pancreatitis and diabetes. By mitigating inflammation, turmeric supports overall pancreatic health and function.
Moreover, curcumin enhances insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels. Improved insulin sensitivity reduces the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, supporting metabolic health.
To benefit from turmeric, incorporate it into curries, stews, soups, or golden milk. Pairing turmeric with black pepper enhances the absorption of curcumin, maximizing its bioavailability and health benefits.

4. Broccoli
Broccoli is a cruciferous vegetable rich in sulforaphane, a compound known for its anti-cancer properties and ability to support detoxification processes in the pancreas. Sulforaphane activates enzymes that detoxify carcinogens and harmful compounds, reducing the risk of pancreatic cancer and supporting overall pancreatic health.
Additionally, broccoli is high in fiber, vitamins C and K, folate, and minerals such as potassium and manganese. Fiber aids digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels, while vitamins and minerals support immune function, bone health, and energy metabolism.
Enjoy broccoli steamed, roasted, or sautéed as a side dish or main component of salads, soups, stir-fries, and casseroles. Eating broccoli raw or lightly cooked preserves its nutrients and health-promoting properties.

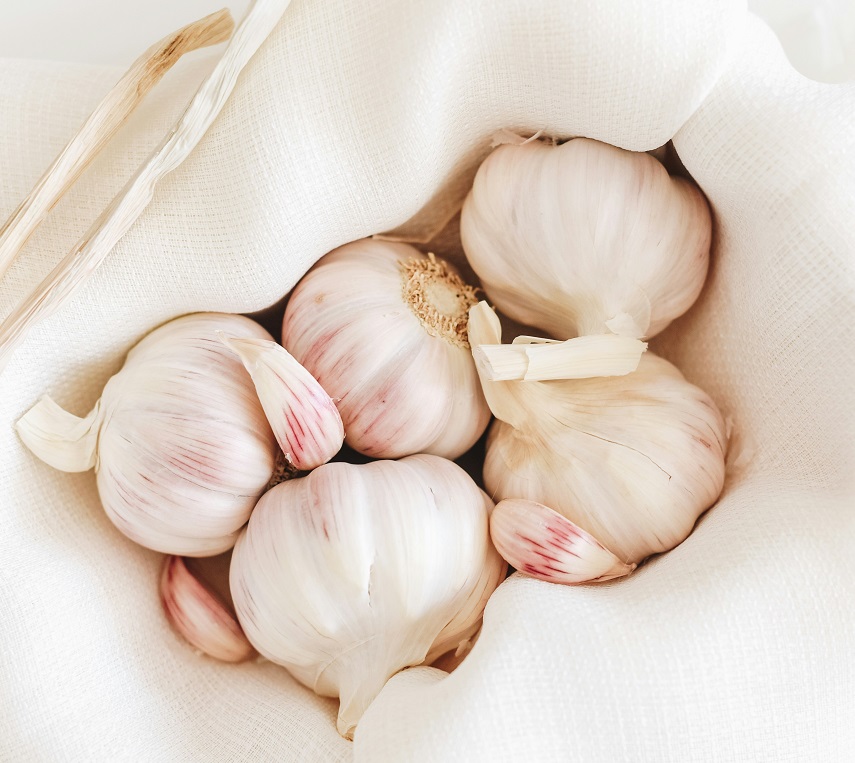
5. Garlic
Garlic has been used for centuries for its culinary and medicinal properties. It contains sulfur compounds, including allicin, which have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects beneficial for pancreatic health.
Antioxidants in garlic help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in pancreatic tissues, protecting cells from damage. This oxidative protection supports overall pancreatic function and may reduce the risk of pancreatic disorders.
Garlic’s anti-inflammatory properties help mitigate inflammation in the pancreas, which is beneficial for preventing and managing pancreatic diseases such as pancreatitis and diabetes.
Incorporate garlic into your diet by adding it to sauces, soups, stir-fries, roasted vegetables, or homemade dressings. Crushing or chopping garlic cloves before cooking enhances the formation of beneficial compounds like allicin.

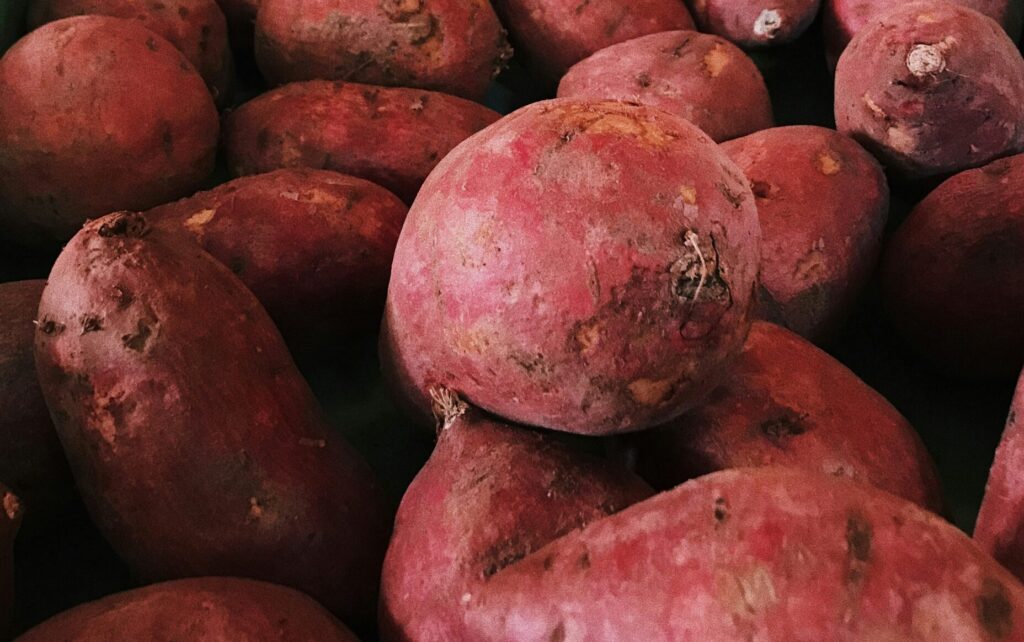
6. Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes are nutrient-dense root vegetables rich in beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A, which supports immune function and maintains healthy pancreatic tissues. Beta-carotene acts as an antioxidant, protecting pancreatic cells from oxidative stress and inflammation.
Additionally, sweet potatoes provide fiber, vitamins C and B6, potassium, and manganese. Fiber aids digestion and regulates blood sugar levels, while vitamins and minerals support overall metabolic health and immune function.
Enjoy sweet potatoes baked, roasted, steamed, or mashed as a nutritious side dish or main component of meals. Their natural sweetness makes them a versatile ingredient in both savory and sweet dishes.

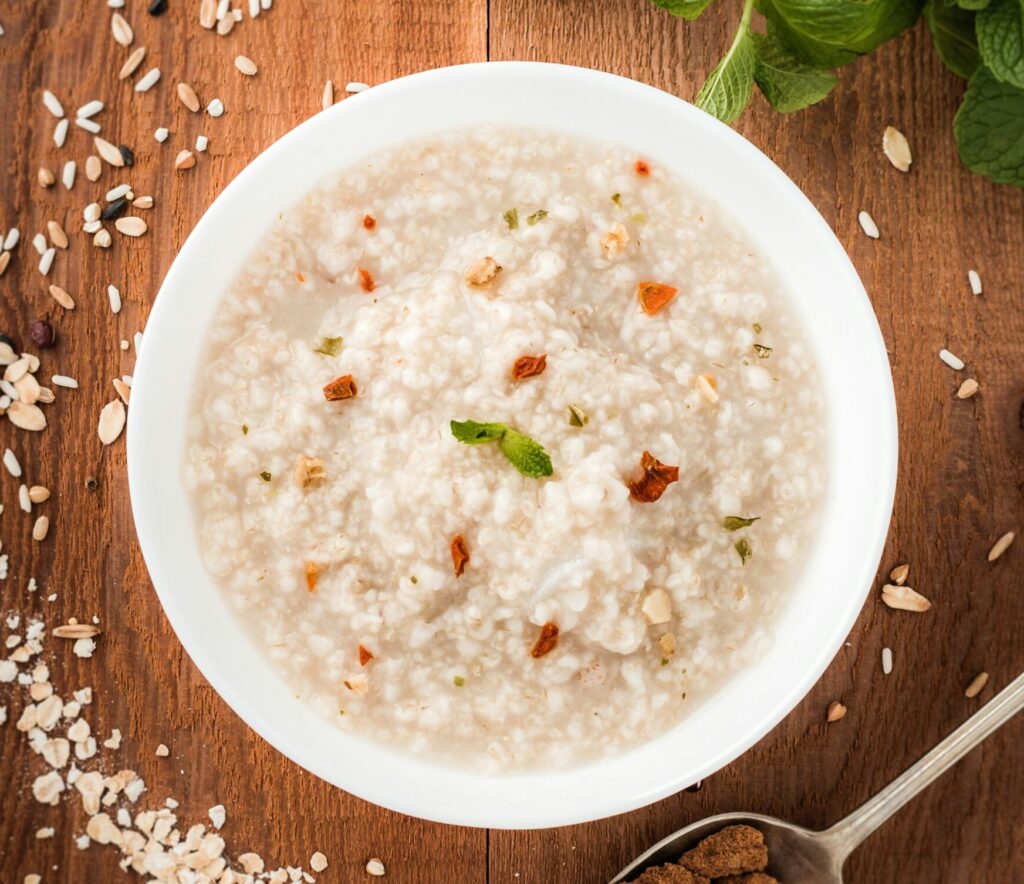
7. Oatmeal
Oatmeal is a whole grain known for its high fiber content and complex carbohydrates, which support pancreatic health and blood sugar regulation. The soluble fiber in oatmeal forms a gel-like substance in the digestive tract, slowing down digestion and promoting satiety.
By slowing digestion, oatmeal helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of insulin resistance. Stable blood sugar levels lessen the burden on the pancreas to produce insulin, supporting overall pancreatic function.
Oatmeal also contains beta-glucan, a type of soluble fiber that has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity. Improved insulin sensitivity enhances the body’s ability to utilize insulin effectively, crucial for metabolic health.
Incorporate oatmeal into your diet as a breakfast cereal, overnight oats, or blended into smoothies. Customize your oatmeal with toppings like fresh fruits, nuts, seeds, and a drizzle of honey or maple syrup for added flavor and nutritional benefits. – Mohit Tandon Burr Ridge

8. Yogurt
Yogurt is a fermented dairy product rich in probiotics—beneficial bacteria that support gut health and indirectly benefit pancreatic function. Probiotics help maintain a healthy balance of gut microbiota, essential for proper digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function.
A healthy gut microbiome contributes to overall pancreatic health by reducing inflammation in the digestive tract and supporting optimal nutrient metabolism.
Yogurt is also a good source of protein, calcium, vitamins B12 and D, and other essential nutrients. Protein supports muscle repair and growth, while calcium and vitamins contribute to bone health and immune function.
Choose plain yogurt with live and active cultures to maximize probiotic benefits. Enjoy yogurt on its own, with fresh fruits, or as a base for smoothies, parfaits, and dips.

9. Olive Oil
Olive oil is a key component of the Mediterranean diet, known for its numerous health benefits, including its positive effects on pancreatic health. Rich in monounsaturated fats, particularly oleic acid, olive oil has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce inflammation in pancreatic tissues.
Chronic inflammation in the pancreas is associated with various pancreatic disorders, including pancreatitis and diabetes. By mitigating inflammation, olive oil supports overall pancreatic function and helps protect pancreatic cells from damage.
Moreover, olive oil is rich in antioxidants, such as polyphenols and vitamin E, which further contribute to its anti-inflammatory effects and protect pancreatic cells from oxidative stress.
To incorporate olive oil into your diet, use it for cooking, salad dressings, and drizzling over vegetables or whole grains. Choose extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) for its higher levels of antioxidants and beneficial compounds compared to refined olive oils.

10. Salmon
Salmon is a fatty fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), which have numerous health benefits for pancreatic health and overall well-being.
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that the body cannot produce on its own, so they must be obtained from the diet. These fats have potent anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce inflammation in pancreatic tissues and support overall pancreatic function.
Moreover, omega-3 fatty acids improve insulin sensitivity, crucial for regulating blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of insulin resistance—a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
Salmon is also a good source of high-quality protein, vitamins D and B12, and minerals such as selenium and potassium. Protein supports muscle repair and growth, while vitamins and minerals contribute to immune function and energy metabolism.
Incorporate salmon into your diet at least twice a week to benefit from its omega-3 fatty acids and other essential nutrients. Enjoy grilled, baked, or broiled salmon with herbs, lemon, and olive oil for a flavorful and nutritious meal.
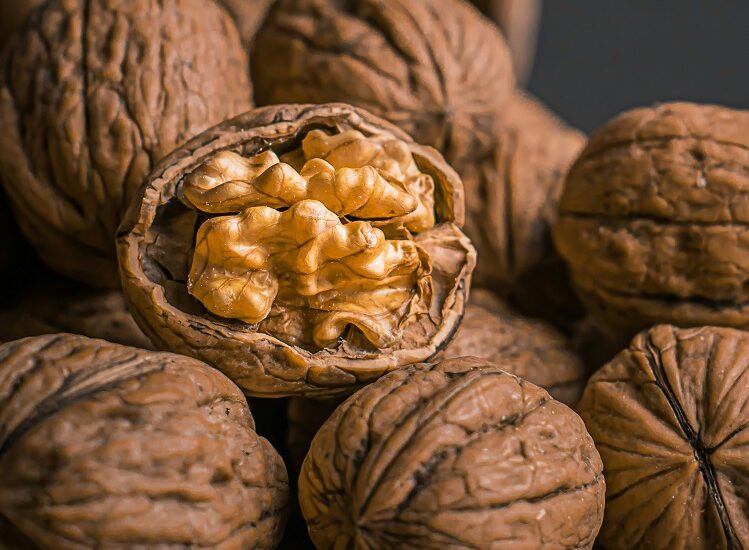
11. Walnuts
Walnuts are nutrient-dense nuts packed with omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals that support pancreatic health and overall well-being.
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), in walnuts have potent anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce inflammation in pancreatic tissues and support overall pancreatic function. These fats also improve insulin sensitivity, crucial for regulating blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of insulin resistance.
Moreover, walnuts are rich in antioxidants, such as polyphenols and vitamin E, which help neutralize free radicals and protect pancreatic cells from oxidative stress.
Walnuts provide a good source of plant-based protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, including magnesium, copper, and manganese. Protein supports muscle repair and growth, while vitamins and minerals contribute to immune function and antioxidant defense systems.
Incorporate walnuts into your diet as a snack, or add them to salads, oatmeal, yogurt, and baked goods for a crunchy and nutritious boost. Aim to include a variety of nuts and seeds in your diet to benefit from their unique nutrient profiles and health-promoting properties. – Mohit Tandon Burr Ridge

12. Green Tea
Green tea is a popular beverage rich in antioxidants, particularly catechins, which offer numerous health benefits for pancreatic health and overall well-being.
Catechins in green tea have potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that help reduce inflammation in pancreatic tissues and protect pancreatic cells from oxidative stress. These compounds also support immune function and help maintain cellular integrity throughout the body.
Moreover, green tea contains epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a catechin studied for its potential therapeutic effects on pancreatic disorders, including pancreatitis and diabetes. EGCG may help regulate blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce the risk of insulin resistance.
Green tea is low in calories and rich in polyphenols, contributing to its health-promoting properties and supporting overall pancreatic function.
To benefit from green tea, drink several cups daily as part of a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle. Enjoy green tea hot or cold, with or without added flavors like lemon or mint, to suit your preferences.

13. Lentils
Lentils are legumes rich in protein, fiber, complex carbohydrates, and essential nutrients that support pancreatic health and overall well-being.
The high fiber content in lentils helps regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. This prevents rapid spikes in blood glucose after meals, reducing the strain on the pancreas to produce insulin and promoting stable energy levels throughout the day.
Moreover, lentils are a good source of plant-based protein, essential for muscle repair, growth, and overall cellular function. Protein also helps regulate appetite and supports metabolic processes, contributing to overall pancreatic health.
Lentils provide a variety of vitamins and minerals, including folate, iron, magnesium, and potassium, essential for energy metabolism, immune function, and antioxidant defense systems.
Incorporate lentils into soups, stews, salads, and casseroles for a hearty and nutritious meal. Choose from different colors and varieties, such as brown, green, red, and black lentils, to enjoy their unique flavors and textures.

14. Avocado
Avocado is a nutrient-dense fruit rich in healthy fats, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support pancreatic health and overall well-being.
The monounsaturated fats in avocado, particularly oleic acid, have anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce inflammation in pancreatic tissues and support overall pancreatic function. These fats also improve insulin sensitivity, crucial for regulating blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of insulin resistance.
Avocado is also a good source of dietary fiber, which supports digestive health, regulates appetite, and helps stabilize blood sugar levels. Fiber promotes satiety and prevents overeating, contributing to weight management and overall pancreatic health.
Additionally, avocados provide vitamins C, E, K, and B-complex vitamins, as well as potassium and magnesium, essential for immune function, bone health, and antioxidant defense systems.
Enjoy avocado sliced on toast, added to salads, blended into smoothies, or mashed as guacamole. Its creamy texture and mild flavor make it a versatile ingredient for both savory and sweet dishes.

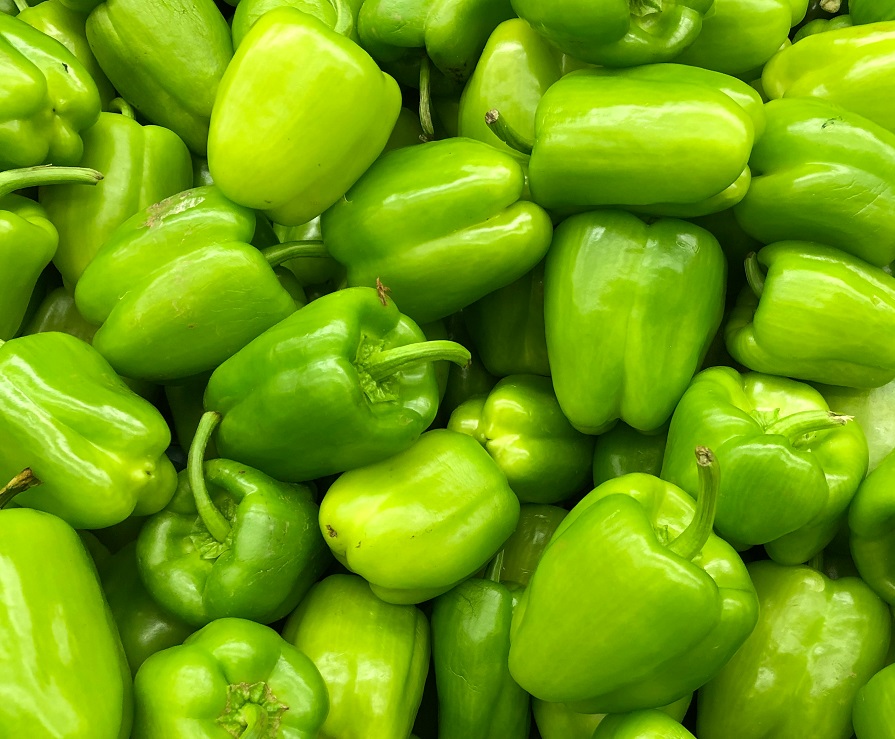
15. Bell Peppers
Bell peppers, particularly the brightly colored varieties like red, yellow, and orange, are rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber that support pancreatic health and overall well-being. These are exceptionally high in vitamin C, an antioxidant that helps protect pancreatic cells from oxidative stress and supports immune function. Vitamin C also enhances the absorption of iron, crucial for energy metabolism and overall metabolic stability.
Moreover, bell peppers provide vitamin A, which supports immune function and maintains healthy skin and vision. They are also a good source of dietary fiber, essential for digestive health and blood sugar regulation.
Incorporate bell peppers into your diet by adding them to salads, stir-fries, soups, and wraps. Enjoy them raw with hummus or roasted with olive oil and herbs for a flavorful and nutritious meal.

